Qatar is one of the fastest-growing job markets in the Gulf. Every year, thousands of skilled and unskilled workers travel here for better income, safe working conditions, and tax-free salaries. To work legally, you need the right visa or permit approved under Qatar’s labor laws. This process involves your employer, the Ministry of Labour, and sometimes the Qatar Visa Center. Understanding each step clearly can help you avoid delays, rejections, or legal problems while starting your career in Doha or other Qatari cities.
Understanding the Qatar Work Visa
A Qatar Work Visa is a legal document issued by the Ministry of Labour that allows foreign nationals to work in the country under a specific sponsor. It connects your employment to Qatar’s labor laws and protects your rights as a worker. Without it, any job in Qatar is considered illegal, and violations can result in fines, deportation, or a work ban.

The visa is always tied to a Qatari employer (sponsor), who is responsible for submitting your application, paying required government fees, and ensuring you meet all immigration rules. This sponsorship system applies to both skilled professionals and unskilled laborers.
Why the Qatar Work Visa Matters
- It ensures you are covered under Qatar’s labor protection system.
- It provides legal permission to work in Qatar.
- It links you to benefits such as healthcare, housing allowance, and end-of-service gratuity.
- It allows you to apply for a Residence Permit (QID) to live in the country.
Expatriate Workforce in Qatar
Qatar’s economy relies heavily on expatriates, who make up the majority of its workforce. From large infrastructure projects to hospitality, healthcare, and education, foreign workers are essential to the country’s growth. According to government data, more than 85% of Qatar’s population consists of expatriates from Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas.

Foreign workers often choose Qatar for its tax-free salaries, modern living standards, and strong labor protections. Many of these jobs are offered under fixed-term contracts, with benefits such as housing allowances, health insurance, and paid annual leave.
Key Sectors Employing Expatriates
- Construction and Infrastructure – Large-scale stadiums, highways, and metro projects.
- Oil and Gas Industry – One of the largest contributors to Qatar’s GDP.
- Hospitality and Tourism – Hotels, restaurants, and event management.
- Healthcare – Hospitals, clinics, and specialized medical centers.
- Education – Schools, universities, and training institutes.
Types of Qatar Work Visas
Qatar offers different types of work visas based on the nature of the job, contract length, and the worker’s profession. Choosing the correct visa type is important because it determines your legal rights, contract terms, and renewal process. Each visa is issued by the Ministry of Labour and sponsored by a registered Qatari employer.

Standard / Employment Visa
This is the most common type of work visa, issued for long-term employment under a Qatari company. It is valid for one to five years and can be renewed. Holders can apply for a Residence Permit (QID) and may be eligible to sponsor family members.
Temporary or Short-Term Work Visa
Granted for short-term assignments or projects, usually lasting one to six months. It is often used for seasonal work, urgent projects, or consultancy roles. Renewal is limited and depends on the employer’s request.
Domestic Worker Visa
Specifically for household staff such as maids, drivers, nannies, and cooks. The employer must be a Qatari citizen or an approved expatriate resident who meets the salary and accommodation requirements.
Business Visa
Issued for individuals visiting Qatar for business meetings, negotiations, or short-term work that does not require long-term residency. Usually valid for one to three months.
Digital Nomad Visa
Introduced to attract remote workers, this visa allows professionals to live in Qatar while working for a foreign employer or operating an online business. Applicants must meet specific income and accommodation criteria.
Requirements for Qatar Work Visa
To get a Qatar Work Visa, applicants must meet specific eligibility conditions set by the Ministry of Labour and immigration authorities. These requirements ensure that workers are qualified for their job role and meet Qatar’s safety, security, and legal standards.
Eligibility Criteria
- Valid Job Offer – You must have a confirmed employment contract from a Qatari company or government entity.
- Sponsorship – An employer (sponsor) registered in Qatar must submit your visa application.
- Professional Qualifications – Relevant education, training, or experience for the job role.
- Clean Legal Record – No criminal history in Qatar or your home country.
Age Limit
- Most professions accept applicants between 21 and 50 years old.
- Certain skilled roles may accept applicants up to 60 years old with approval.
- The maximum age for some labor roles can be lower due to insurance restrictions.
Health and Medical Requirements
- Pre-employment medical examination in your home country or at a Qatar Visa Center (QVC).
- Tests include HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, hepatitis, and general fitness checks.
- Some roles require additional health clearance, such as food handlers or healthcare workers.
Documents Required for Qatar Work Visa
Applying for a Qatar Work Visa requires a set of verified documents from both the employer and the employee. These papers prove your identity, eligibility, and compliance with Qatar’s immigration and labor laws. Missing or incorrect documents can delay approval or lead to rejection.

Employer Documents
- Copy of the company’s Commercial Registration (CR).
- Company Computer Card showing registered signatories.
- Valid Trade License issued by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Work visa quota approval from the Ministry of Labour.
- Signed employment contract, stamped and approved.
Employee Documents
- Valid passport with at least 6 months before expiry.
- Recent passport-sized photographs with white background.
- Educational and professional certificates (attested by your country’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Qatar Embassy).
- Police clearance certificate (PCC) from home country.
- Medical fitness certificate (from QVC or approved clinic).
Attestation and Verification Process
- All academic, professional, and legal documents must be attested by relevant authorities in your home country.
- The final attestation is done by the Qatar Ministry of Foreign Affairs before processing the visa.
Employer’s Role in the Work Visa Process
In Qatar, the employer (sponsor) is legally responsible for initiating and managing the work visa process. Without their involvement, no foreign worker can obtain legal employment status. The Ministry of Labour requires sponsors to follow strict guidelines to protect both the worker and the Qatari job market.
Sponsorship and Quota Approval
- Employers must have a valid Commercial Registration (CR) and an active Trade License.
- They must apply for work visa quota approval to determine the number and types of foreign workers they can hire.
- Quota requests are reviewed based on the company’s size, industry, and labor market needs.
Submitting the Visa Application
- The employer completes and submits the work visa application to the Ministry of Labour.
- Required employer and employee documents are attached for verification.
- Most applications are processed electronically through Qatar’s Hukoomi portal.
Covering Visa Costs
- Under Qatari labor law, the employer is responsible for paying all government fees related to the work visa.
- This includes medical tests, biometric registration, and the issuance of the Residence Permit (QID).
Step-by-Step Qatar Work Visa Application Process
Obtaining a Qatar Work Visa is a coordinated process between the employer (sponsor), the Ministry of Labour, and the Ministry of Interior. Every step must be completed in sequence, and all documents must be accurate and fully attested. Even a small error, such as an expired passport or mismatched document details, can delay or cancel the visa approval.
Step 1: Quota Approval from the Ministry of Labour
Before hiring a foreign worker, the employer must request work visa quota approval. This determines how many expatriates they are allowed to employ and in what job categories. The request is evaluated based on:
- The size and legal status of the company.
- The demand for the worker’s profession in Qatar’s labor market.
- Compliance with previous labor and immigration regulations.
Without quota approval, the employer cannot proceed to the next stage.
Step 2: Drafting and Signing the Employment Contract
Once the quota is granted, the employer prepares a formal employment contract. This includes:
- Basic salary and additional allowances (housing, transport, etc.).
- Job title, duties, and location of work.
- Contract length (fixed-term or unlimited).
- Entitlements such as annual leave, medical insurance, and end-of-service benefits.
The contract must be signed by both parties and later registered with the Ministry of Labour.
Step 3: Submitting the Visa Application
The employer submits the work visa application through the Hukoomi e-government portal or at the immigration department. Required documents include the company’s Commercial Registration, trade license, employee’s attested educational certificates, passport copies, and passport photographs. The Ministry of Labour reviews the application to verify authenticity and eligibility.
Step 4: Visa Approval and Issuance
If the application meets all requirements, the Ministry of Interior issues an electronic visa (e-visa). This visa is sent to the employer, who forwards it to the employee for use during travel. It is important to check the validity dates and ensure the visa is used before it expires.
Step 5: Medical Examination and Biometric Registration
The employee must complete a medical test and biometric registration either:
- Before arrival at a Qatar Visa Center (QVC) in their home country.
- After arrival at an approved medical facility in Qatar.
The medical test screens for conditions like HIV, tuberculosis, hepatitis, and other communicable diseases. Biometric registration records fingerprints and facial images in the Ministry of Interior’s database.
Step 6: Entry into Qatar and Residence Permit (QID) Processing
Once the worker enters Qatar, the employer has a limited period (usually within 7–30 days) to apply for the Residence Permit (QID). This involves:
- Submitting the employee’s passport and medical clearance.
- Completing fingerprint verification at the Ministry of Interior.
- Paying the government fees for the QID issuance.
The Residence Permit is the worker’s official identification in Qatar and is required for opening bank accounts, renting accommodation, and accessing most services.
Medical Examination and Health Requirements
Qatar’s immigration authorities place strong emphasis on the health screening process to protect public safety and ensure workers are physically fit for their assigned duties. The medical examination is a mandatory step for all foreign workers applying for a Qatar Work Visa and is closely monitored by the Ministry of Public Health (MoPH).
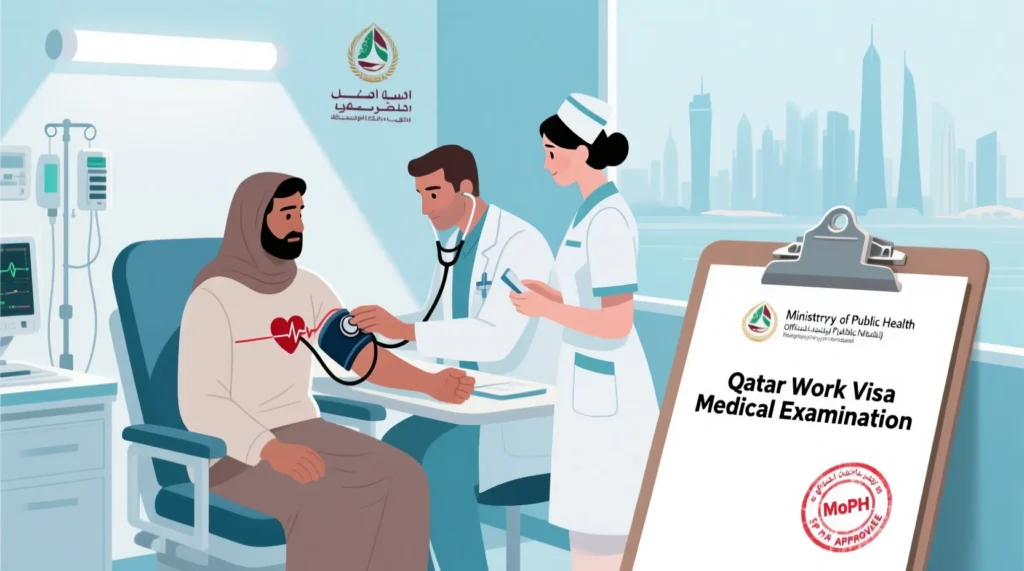

The medical process checks for communicable diseases and evaluates overall physical fitness. It applies equally to workers undergoing pre-departure screening in their home country and those completing it after arrival in Qatar.
Mandatory Health Tests
The medical examination typically includes:
- Blood Tests – Screening for HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, and other infectious diseases.
- Chest X-Ray – Detects tuberculosis or other lung-related conditions.
- General Physical Examination – Measures vital signs, body mass index (BMI), and checks for chronic illnesses.
Some professions such as food handlers, healthcare workers, and domestic staff may require additional medical tests or vaccination records.
Where and When to Take the Medical Exam
- Before Arrival – Conducted at an approved Qatar Visa Center (QVC) in selected countries like India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Philippines.
- After Arrival – For workers coming from countries without QVC facilities, the exam must be completed at a MoPH-approved clinic in Qatar.
Passing the Medical Test
If the worker is found medically fit, the results are automatically sent to the Ministry of Interior for further visa processing.
If unfit, the visa application is canceled, and the worker cannot legally enter or remain in Qatar for employment purposes.
Nationality-Specific Requirements
While Qatar’s general work visa rules apply to all foreign workers, certain nationalities have additional procedures due to bilateral agreements, recruitment regulations, and health protocols. These nationality-specific requirements are enforced by both Qatar’s Ministry of Labour and the worker’s home country labor department.
India
- Emigration Clearance – Indian workers in specific job categories must obtain clearance from the Protector of Emigrants (POE) through the eMigrate portal before departure.
- Pre-Departure Orientation Programme (PDOT) – Mandatory training on Qatar’s labor laws, cultural norms, and worker rights.
- Qatar Visa Center (QVC) in India – All medical tests, biometric registration, and contract signing are completed here before travel.
Nepal
- Workers must register with the Department of Foreign Employment (DOFE) and receive an official labor permit.
- Mandatory orientation training on workplace safety, rights, and living in Qatar.
- Medical tests conducted in DOFE-approved clinics before departure.
Philippines
- All contracts for Filipino workers must be verified by the Philippine Overseas Employment Administration (POEA) or the Department of Migrant Workers (DMW).
- Attendance in the Pre-Departure Orientation Seminar (PDOS) is required.
- Deployment only through POEA-accredited recruitment agencies.
Bangladesh
- Workers must obtain clearance from the Bureau of Manpower, Employment and Training (BMET).
- Registration on the BMET database is required before a work visa can be processed.
- Medical screening in BMET-approved health centers.
Other Nationalities
- Some countries require exit permits or special endorsements before workers can leave for Qatar.
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) agreements may simplify procedures for citizens of neighboring states.
These additional steps help ensure that workers are legally protected, contracts are verified, and both governments are informed about overseas employment movements.
Cost of Qatar Work Visa
The cost of obtaining and maintaining a Qatar Work Visa depends on several factors, including the type of job, the applicant’s nationality, and whether the process is handled in Qatar or through a Qatar Visa Center (QVC) abroad. All government fees are regulated by the Ministry of Interior and Ministry of Labour, and in most cases, employers are responsible for covering these costs under Qatari labor law.
Application Fees
- Work Visa Fee – Generally around QAR 200–300 for the initial visa issuance.
- Medical Examination – At a QVC abroad, fees range from QAR 300–500 depending on the country. In Qatar, the MoPH standard medical test costs about QAR 100.
- Biometric Registration – Usually included in the visa processing fee at QVCs, or QAR 150–200 when done in Qatar.
- Residence Permit (QID) Issuance – QAR 1,000 per year for standard work permits.
In many cases, employers cover these expenses in full. However, workers should confirm this before signing the contract to avoid misunderstandings.
Renewal Fees
- Annual Renewal of Residence Permit – QAR 1,000 for employees, paid by the employer in most cases.
- Medical Re-Examination – Required if the permit has lapsed for an extended period; cost varies between QAR 100–300.
- Late Renewal Penalties – The Ministry of Interior charges a daily fine (typically QAR 10 per day) for overstaying without a valid permit.
Proper budgeting for these costs is important, especially for workers who may need to renew multiple times during their employment contract in Qatar.
Processing Time for Qatar Work Visa
The time it takes to process a Qatar Work Visa depends on the applicant’s nationality, the employer’s compliance history, and whether all documents are correctly prepared. The Ministry of Labour and Ministry of Interior oversee each stage, and delays often occur if documentation is incomplete or requires additional verification.
Typical Duration
- For most applicants, the process takes 2 to 4 weeks from the time the employer submits the application to visa approval.
- If a Qatar Visa Center (QVC) is involved, pre-departure medical tests, biometrics, and contract signing can reduce arrival procedures but may add 5–10 days before departure.
- Peak recruitment seasons (e.g., before large construction projects or events) can extend processing times due to higher application volumes.
- Applications flagged for extra background checks by the Ministry of Interior may take longer, sometimes up to 6–8 weeks.
Renewal Timeframes
- Renewing a Residence Permit (QID) is generally faster, often completed within 3–5 working days once the renewal request is submitted online through the Hukoomi portal.
- Employers are advised to initiate renewal at least 30 days before the permit’s expiry to avoid late penalties.
- If a medical re-examination is required for renewal (in rare cases), this can add 2–3 extra days to the process.
Efficient processing depends on the employer’s preparation, timely submission, and compliance with all government requirements. Workers can speed things up by ensuring that passports, medical certificates, and other documents are valid and properly attested before the application begins.
Validity and Renewal of Qatar Work Visa
A Qatar Work Visa is generally issued for one to three years, depending on the employment contract and the employer’s request to the Ministry of Interior (MOI). The validity period is clearly stated on the worker’s Residence Permit (QID), which serves as both an ID card and proof of legal employment in Qatar.
Initial Validity
- Standard Duration – Most work visas are granted for 1 year initially, with the option to extend annually.
- Project-Based Contracts – Workers hired for short-term projects may receive visas valid for 3–6 months only.
- Special Professions – Certain categories like engineers, medical professionals, and senior executives may receive multi-year visas in line with longer contracts.
Renewal Process
Renewal is handled by the employer and involves submitting an online request via the Hukoomi portal or directly at an MOI service center. Required steps include:
- Payment of Renewal Fee – QAR 1,000 per year for employees.
- Medical Clearance (if applicable) – In rare cases, workers may be asked to undergo a re-examination.
- MOI Approval – Updated details are printed on the new QID card.
Employers should start the renewal process at least 30 days before expiry to avoid penalties and ensure uninterrupted legal status for the worker.
Penalties for Late Renewal
The MOI charges a fine of approximately QAR 10 per day for overstaying after the permit expires. This penalty is calculated until the day the renewal is completed or the worker leaves Qatar.
Maintaining a valid QID is essential not only for legal employment but also for accessing housing, healthcare, banking, and other essential services in Qatar.
Reasons for Qatar Work Visa Rejection and How to Avoid Them
Even if an employer submits all documents on time, the Ministry of Labour or Ministry of Interior (MOI) can reject a Qatar Work Visa application if certain requirements are not met. Understanding these common reasons, and how to avoid them can save weeks of delays and unnecessary expenses.
1. Incomplete or Incorrect Documentation
- Common issue: Missing passport copies, unverified educational certificates, or unsigned employment contracts.
- Prevention: Double-check that all documents are attested by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in the worker’s home country and verified by the Qatari Embassy before submission.
2. Mismatched Information
- Common issue: Spelling errors in the applicant’s name, passport number, or date of birth.
- Prevention: Ensure all forms, contracts, and certificates match the details in the passport exactly, even a small typo can trigger rejection.
3. Failure to Meet Health Requirements
- Common issue: Workers failing medical tests for conditions like HIV, tuberculosis, or hepatitis B/C.
- Prevention: Take the medical examination at a Qatar Visa Center (QVC) or a Ministry of Public Health-approved clinic before travel to confirm fitness.
4. Quota Restrictions
- Common issue: Employer’s visa quota for a specific job category is already full.
- Prevention: Employers should apply for quota approval early through the Labour Department before hiring.
5. Employer Non-Compliance
- Common issue: Companies with unpaid fines, expired licenses, or previous labor law violations may have visa requests denied.
- Prevention: Work only with employers who have valid Commercial Registration (CR), trade license, and a clean compliance record.
6. Security or Background Check Failure
- Common issue: Applicant flagged due to a past criminal record or immigration violation.
- Prevention: Resolve any pending legal matters and ensure there is no travel ban or previous overstay history in Qatar or GCC countries.
By preparing complete, accurate documents, meeting all health standards, and working with compliant employers, applicants can significantly improve their chances of visa approval.
Changing Jobs in Qatar
Foreign workers in Qatar are allowed to change employers under specific rules set by the Ministry of Labour and the Ministry of Interior (MOI). Over the past few years, significant reforms have made job mobility easier, removing some of the older restrictions that tied workers to a single sponsor.
NOC Requirements & Recent Changes
- Before 2020 – Workers needed a No Objection Certificate (NOC) from their current employer to transfer to another company before the contract ended. Without it, they could not legally switch jobs in Qatar.
- Post-2020 Reforms – Under the updated Labour Law (Law No. 18 of 2020), the NOC requirement was abolished. Workers can now change jobs without their employer’s permission, provided they give the required notice.
- Notice Periods –
- Within probation period: At least 1 month’s notice.
- After probation: 2 months’ notice for indefinite contracts, unless otherwise specified in the contract.
- Online Job Change Process –
- Submit a job change request through the Ministry of Labour’s online platform.
- Upload the new employment contract and any required documents.
- Wait for MOI approval and issuance of a new Residence Permit (QID) under the new employer.
- Exceptions – Workers in certain sensitive industries or under fixed-term project contracts may have additional restrictions or require special approval.
These reforms have increased job market flexibility, aligned Qatar’s labor system with International Labour Organization (ILO) standards, and strengthened worker rights. However, it’s still essential for workers to follow proper procedures to avoid legal or visa complications.
Working Hours & Minimum Wage in Qatar
Employment conditions in Qatar are regulated by the Labour Law (Law No. 14 of 2004), with updates introduced by the Ministry of Labour to protect workers’ rights and align with international labor standards. These regulations define maximum working hours, rest periods, and minimum wage requirements for all employees, regardless of nationality.
Standard Working Hours
- The legal maximum is 48 hours per week, typically 8 hours per day over six days, with Friday as the official weekly rest day.
- During the holy month of Ramadan, working hours are reduced to 36 hours per week for all employees, regardless of faith.
- Workers are entitled to at least one hour of rest for every five consecutive hours worked.
- For certain industries like construction, additional restrictions apply in summer under the Midday Work Ban, prohibiting outdoor work between 10:00 a.m. and 3:30 p.m. from June to mid-September.
Overtime Rules
- Any work beyond the standard hours must be compensated at 125% of the basic hourly wage.
- If overtime is worked during holidays or rest days, pay increases to 150% of the basic hourly rate.
Minimum Wage
- Introduced in March 2021, Qatar’s minimum wage applies to all workers, regardless of sector or nationality.
- The current rate is QAR 1,000 per month as a base salary.
- Employers must also provide:
- QAR 300 monthly for food allowance (if meals aren’t provided).
- QAR 500 monthly for accommodation allowance (if housing isn’t provided).
- Employers failing to meet the minimum wage requirement can face penalties under MOI and Ministry of Labour enforcement measures.
By enforcing strict rules on working hours and pay, Qatar aims to ensure fair treatment for all employees while maintaining productivity across its workforce.
Benefits of Having a Qatar Work Visa
Holding a Qatar Work Visa offers more than just legal permission to work; it opens the door to a range of financial, lifestyle, and family advantages that make the country an attractive destination for expatriates. These benefits are backed by Qatar’s Labour Law and government initiatives designed to attract skilled workers from around the world.
Tax-Free Income
- One of the biggest draws for foreign professionals is that Qatar imposes no personal income tax on salaries or wages.
- This means employees take home their full contractual pay, without deductions for income tax, social security, or pension contributions.
- The Ministry of Finance maintains this policy to make Qatar competitive in attracting global talent, particularly in sectors like oil & gas, engineering, and healthcare.
Housing & Travel Benefits
- Many employers, especially in large corporations or government projects, provide fully furnished housing or a monthly housing allowance.
- Some contracts include annual paid flights to the employee’s home country, covering both the worker and their dependents.
- Transportation benefits such as company cars, fuel allowances, or shuttle services are common in certain industries.
Family Sponsorship
- A valid work visa allows employees earning the minimum salary threshold (currently QAR 10,000 per month, or QAR 7,000 with employer-provided housing) to sponsor immediate family members for residence in Qatar.
- The process is handled through the Ministry of Interior’s Immigration Department and typically requires proof of accommodation and health insurance for dependents.
- Family sponsorship enables spouses and children to access education, healthcare, and other public services, making relocation more comfortable and sustainable for long-term stays.
Do GCC Citizens Need a Qatar Work Visa?
Citizens of Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) member states Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates enjoy special mobility rights in Qatar under regional agreements. According to the GCC Common Market framework, these nationals do not require a traditional Qatar Work Visa to be employed in the country.
Instead of going through the standard visa sponsorship process, GCC citizens can:
- Enter Qatar using their national ID card or passport without a pre-arranged work permit.
- Apply directly for a Qatari Residence Permit (QID) once they secure employment.
- Work in Qatar without quota restrictions that apply to non-GCC foreign workers.
Employment Process for GCC Nationals
- The employer still needs to register the employee with the Ministry of Labour for compliance and payroll purposes.
- A QID must be issued for access to healthcare, banking, and housing services.
- While no medical test is required before entry, GCC nationals may need to undergo a health check at a Ministry of Public Health-approved clinic before the QID is issued.
This streamlined arrangement is part of broader GCC economic integration efforts, allowing skilled professionals and businesses to move freely across member states.
Residency Permit in Qatar (QID)
Once a foreign worker arrives in Qatar on a valid work visa, obtaining a Residency Permit, also called the Qatar ID (QID) is the next essential step. This document, issued by the Ministry of Interior (MOI), serves as both proof of legal residency and the official work authorization for the duration of the employment contract. Without a QID, a worker cannot access key services such as healthcare, banking, housing contracts, or mobile phone registration.
How to Obtain
- Employer’s Responsibility – The sponsoring company is legally required to initiate the QID application within the worker’s first 7 days in Qatar.
- Medical Examination – Conducted at a Ministry of Public Health-approved medical center, this includes blood tests, chest X-rays, and screening for communicable diseases.
- Biometric Registration – Fingerprints and facial photographs are taken at the MOI fingerprint department.
- Application Submission – The employer submits the completed forms and medical clearance to the MOI, either online via the Hukoomi portal or at an MOI service center.
- Issuance of QID – Once approved, the QID card is printed and delivered, usually within a week.
Required Documents
- Original passport of the employee (valid for at least 6 months).
- Work visa copy issued by the MOI.
- Employer’s Commercial Registration (CR) copy.
- Company Immigration Card and establishment details.
- Completed medical clearance certificate from an authorized clinic.
- Biometric receipt from the MOI fingerprint department.
- Passport-size photographs meeting MOI specifications.
Holding a valid QID is mandatory at all times. Workers are required to carry it when accessing government services, traveling within the GCC, or in any official transaction.
Rights & Responsibilities of Foreign Workers in Qatar
Foreign workers in Qatar are protected under the Labour Law (Law No. 14 of 2004) and subsequent reforms introduced by the Ministry of Labour. These laws aim to ensure fair treatment, safeguard health and safety, and maintain a balanced relationship between employers and employees. While workers enjoy significant rights, they are also expected to fulfill specific legal obligations during their stay.

Worker Rights
- Fair Wages – Every employee is entitled to receive at least the national minimum wage (QAR 1,000 basic salary + allowances) as mandated by the Ministry of Labour.
- Safe Working Conditions – Employers must comply with occupational health and safety standards, providing protective gear where required.
- Rest & Leave – Workers have the right to a weekly rest day, paid annual leave, sick leave, and public holidays in accordance with their contract.
- End-of-Service Benefits – Upon contract completion, workers are entitled to gratuity pay calculated based on their length of service.
- Job Mobility – Under recent reforms, workers can change jobs without employer permission, provided they follow the official notice period process.
- Access to Justice – Disputes can be filed with the Labour Dispute Settlement Committee for free resolution services.
Worker Responsibilities
- Compliance with Qatari Laws – Workers must follow all laws, including immigration rules, labor regulations, and public conduct guidelines.
- Fulfilling Contractual Duties – Performing assigned job responsibilities professionally and within agreed hours.
- Notice for Job Changes – Providing the legally required notice before resigning or transferring to another employer.
- Respect for Cultural Norms – Observing Qatari customs, dress codes, and workplace etiquette.
- Safeguarding Company Property – Taking care of employer-provided tools, equipment, or accommodation facilities.
- Keeping Documents Updated – Ensuring the Qatar ID (QID), health card, and other official records remain valid throughout their stay.
Balancing rights with responsibilities not only ensures legal compliance but also helps foreign workers build a positive professional reputation in Qatar.
Visa Requirements for Digital Nomads in Qatar
Digital nomads remote workers who travel while maintaining their jobs are increasingly interested in Qatar due to its strategic location, modern infrastructure, and high quality of life. However, Qatar’s visa and work permit system is traditionally designed around sponsored employment, so digital nomads must understand specific visa options and legal requirements before working remotely from Qatar.

Types of Visas Available to Digital Nomads
- Tourist Visa: Most digital nomads initially enter Qatar on a tourist visa, which typically allows stays up to 30 days with the possibility of extension. This visa does not grant the legal right to work for a Qatari company or provide local services.
- Business Visa: For freelancers or consultants planning short-term business activities, a business visa can sometimes be obtained. This visa allows attending meetings, conferences, and business development activities but prohibits direct employment.
- Remote Work or Digital Nomad Visa (In Progress): As of 2026, Qatar is exploring the introduction of a dedicated digital nomad visa to attract global remote workers. This program aims to provide a legal framework allowing digital nomads to reside and work remotely for foreign companies while enjoying Qatar’s amenities. Stay updated through the Ministry of Interior (MOI) and Qatar Tourism Authority websites for official announcements.
Key Requirements for Digital Nomads
- Valid Passport: Travelers must hold passports valid for at least six months beyond intended stay.
- Proof of Remote Employment: Evidence of employment with a foreign company or ownership of an international business is often required.
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive health insurance coverage valid in Qatar is mandatory.
- Sufficient Financial Means: Proof of sufficient funds to support oneself during the stay is essential.
- No Local Employment: Digital nomads must not engage in local employment or business activities that require Qatari work permits.
Legal Considerations
Currently, digital nomads cannot legally work for Qatari companies or provide services to local clients without a proper work visa or permit. Violating visa terms can result in fines, deportation, or bans. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with immigration experts or legal advisors before undertaking remote work activities in Qatar.
Frequently Asked Questions About Qatar Work Visas and Labor Laws in 2026
Is Qatar still issuing work visas in 2026?
Yes, Qatar continues to grant work visas throughout 2026. The government has simplified procedures to speed up approvals, including online applications and multiple-entry visas valid for up to a year. Employers must also provide health insurance for their workers as part of the visa requirements.
What are the new labor laws regarding job changes in Qatar?
Qatar recently removed the No Objection Certificate (NOC) requirement for changing jobs. This means employees can switch employers after giving proper notice, making job mobility easier and more worker-friendly than before.
Are NOCs still necessary to change jobs in Qatar?
No, the updated regulations eliminate the need for an NOC. Workers can now transfer their sponsorship legally by following the official notification process without requiring employer consent.
Can Pakistani nationals apply for Qatar work visas in 2026?
Absolutely, Pakistani citizens remain eligible for Qatar work visas. The process involves securing a job offer, completing medical tests, and obtaining a residence permit. Typically, processing takes around six weeks.
What are the key points of Qatar’s labor law in 2026?
The labor law sets a minimum wage of QAR 1,000 plus allowances, guarantees overtime pay at 125% of the hourly rate, and protects worker rights like paid leave and job mobility. The law also supports fair workplace conditions and dispute resolution.
Is there a limit on the number of visas issued in 2026?
Currently, Qatar does not impose a fixed limit on work visas for 2026. Visa approvals depend on the applicant’s eligibility, health clearances, and valid sponsorship.
Are work visa slots open for 2026 applications?
Yes, applicants can submit visa applications for 2026. Meeting all requirements and submitting accurate documents is key to a smooth process.
What major events are happening in Qatar in 2026?
Qatar will host events like the Doha International Book Fair, the Qatar International Food Festival, and National Sports Day, showcasing culture, cuisine, and sports.
What is the skilled visa program in Qatar for 2026?
Qatar’s skilled visa targets professionals in sectors like healthcare, technology, and engineering. Applicants must have relevant qualifications, experience, and a job offer from a Qatari employer.
What is Qatar’s unemployment rate expected to be in 2026?
Qatar traditionally has one of the lowest unemployment rates globally, near 0.1%. While exact 2026 figures are not yet out, the trend suggests stable employment levels.
Conclusion
Qatar’s work visa system in 2026 continues to be streamlined and efficient, opening new doors for professionals seeking employment opportunities in the country. Recent updates to labor laws have strengthened worker rights and made it easier for employees to change jobs without unnecessary obstacles, reflecting Qatar’s commitment to a more worker-friendly environment.
For Pakistani nationals and other foreign workers, the visa process remains accessible and well-structured, offering a smooth pathway to build a successful career. With Qatar’s vibrant economy and a calendar full of major cultural and sporting events, 2026 promises ample opportunities for growth and development. Overall, Qatar remains a promising destination for skilled workers aiming for professional advancement and a better quality of life.







2 Comments